
Imagine this. You have knee pain and your GP refers you to an orthopedist. For better diagnostic insight, the orthopedist sends you to a radiology practice to get an MRI done. Based on the report, she then prescribes you with medication and physiotherapy sessions at a clinic to strengthen your knee cartilage. Each of your encounters at the various medical setups generates significant amounts of health data, which is securely stored in one place and can be accessed on a computer or phone. For example, the orthopedist can check your medical history recorded by the GP, the radiologist can refer to the orthopedist's diagnosis and the physiotherapist can access the MRI results stored by the radiologist’s team in their Radiology Information System (RIS). Even though all the practices are using different IT systems internally, your data can be shared and accessed by all the stakeholders involved in the process of your treatment. Curious how? Welcome to the world of healthcare interoperability!
What is healthcare interoperability?
Just like interoperable banking systems offer the ability to access accounts, move money, deposit checks and pay bills - all at the press of a button on your smartphone, healthcare interoperability allows applications, databases, and other computer systems to connect, communicate and exchange information with one another readily, even if they are built on different platforms by different vendors.
Why is it important?
Regardless of where your health journey takes you, your health data should be accessible at all times in all places. However, medical data is only useful if it can be turned into meaningful information that can be processed by humans and machines. This requires standardized data formats, high-quality datasets and seamless communication across IT systems. However, the fact is that a large amount of medical data is hidden in isolated and incompatible systems, making them difficult to exchange, process and interpret. As a result, most healthcare providers fail to use these data for making important clinical or business decisions.
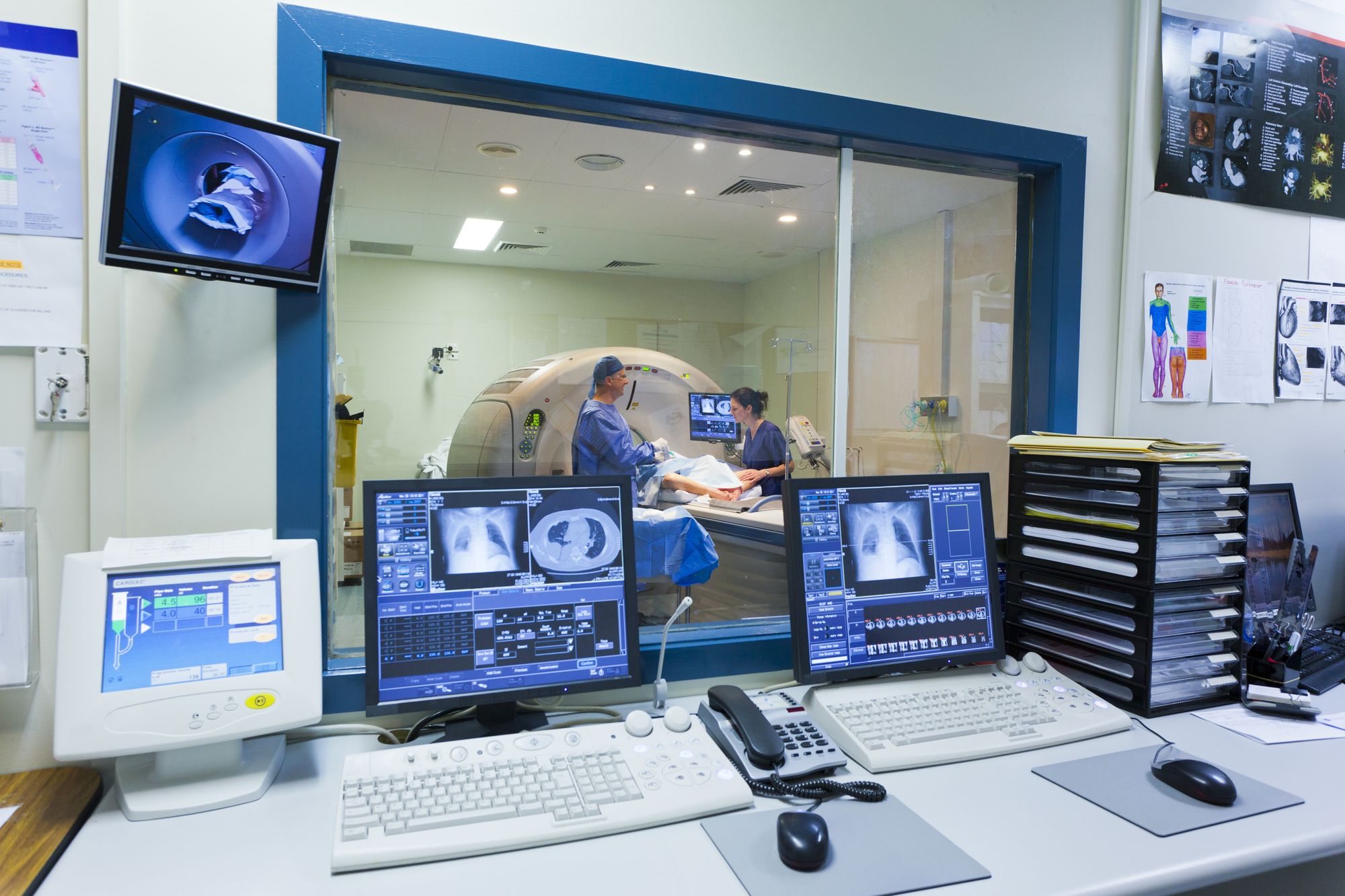
Uncovering the full potential of digital medicine requires international standards for data exchange as well as an interconnected data infrastructure with fast, reliable and secure interfaces. In short, digital medicine depends on interoperable and standardized data. Healthcare interoperability allows disparate IT systems across medical practices and setups to exchange and share data to improve health outcomes. According to HIMSS (Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society), for two systems to be interoperable, they must be able to exchange data and subsequently present that data such that it can be understood by a user. Therefore, many healthcare organizations today are looking to partner with vendors offering next-gen medical imaging, IT and data storage solutions to facilitate data accessibility, interpretation, storage, and exchange. Furthermore, to improve patient care and healthcare productivity, healthcare organizations want vendors to standardize data in usable formats that can be understood by medical practitioners across setups.
How can load balancing help in healthcare interoperability?
Implementing a load balancing solution can help solve communication issues between cumbersome interfaces, data scalability problems and issues related to accessing and connecting data that resides in numerous, often disconnected health data systems located within one setup or spanning across multiple geographical locations. Load balancing can ensure zero downtime by preventing healthcare systems from falling apart whenever there is heavy traffic or data overload, helping clinicians with continuous data access. And additionally reducing workflow interruptions and employee inconveniences caused due to system failures.
As more modalities and newer scanning technologies like 3D mammography are being introduced in hospitals, the storage demand has increased significantly. A load balancer can enable additional storage to be added and seamlessly integrated into a hospital’s storage system to match their massive storage requirements and handle the increasing workload. Most hospitals also face data migration challenges while replacing legacy systems with modern databases. Implementing a load balancer can help in extracting, standardizing, transferring and making data usable for augmenting various digital technologies like AI, analytics, machine learning, etc. Healthcare organizations also face multiple issues around security requirements for accessing certain data. In such cases, a load balancer is able to encrypt the transfer of data from one location to another, allowing users to access that data via a secure connection.

Is interoperability changing the future of healthcare?
While the transition from paper-based charts to electronic health records (EHRs) began almost a decade ago, it is now time for the healthcare industry to pull up their socks and make a quick shift towards interoperability. With mobile, wearable and ingestible health technologies transforming healthcare and medicine, the industry is certainly going to witness an ever-increasing flow of digital health data in the coming years. This combined with cloud computing, big data analytics, AI, etc. can facilitate better diagnostics, faster personalized treatments, and early disease prevention - thus, improving and impacting the lives of millions of patients worldwide.
At Loadbalancer.org, we collaborate directly with our partners, gaining an understanding of their business needs, application requirements and customer challenges. We build load balancing solutions that are integrated into our partners' product infrastructure, enabling them to add a unique value proposition to their offerings. And with our long history of working closely with top healthcare organizations, we can build load balancing solutions uniquely tailored to the needs of the healthcare industry, ensuring zero downtime, standardization, and unlimited scalability.














