Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)

Useful resources
About SMTP servers
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission.
Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages.
Key benefits of load balancing
Here are a few key benefits:
- Ensures the application is always available
- Provides stable, optimal performance
- Ability to isolate servers which reduces risk when performing upgrades/maintenance
- Scalability
How to load balance SMTP servers
The load balancer can be deployed in four fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 SNAT mode.
For SMTP servers, Layer 7 SNAT mode is recommended.
Layer 7 SNAT mode
Layer 7 SNAT mode uses a proxy (HAProxy) at the application Layer. Inbound requests are terminated on the load balancer and HAProxy generates a new corresponding request to the chosen Real Server. As a result, Layer 7 is typically not as fast as the Layer 4 methods.
Layer 7 is typically chosen when either enhanced options such as SSL termination, cookie based persistence, URL rewriting, header insertion/deletion etc are required, or when the network topology prohibits the use of the Layer 4 methods.
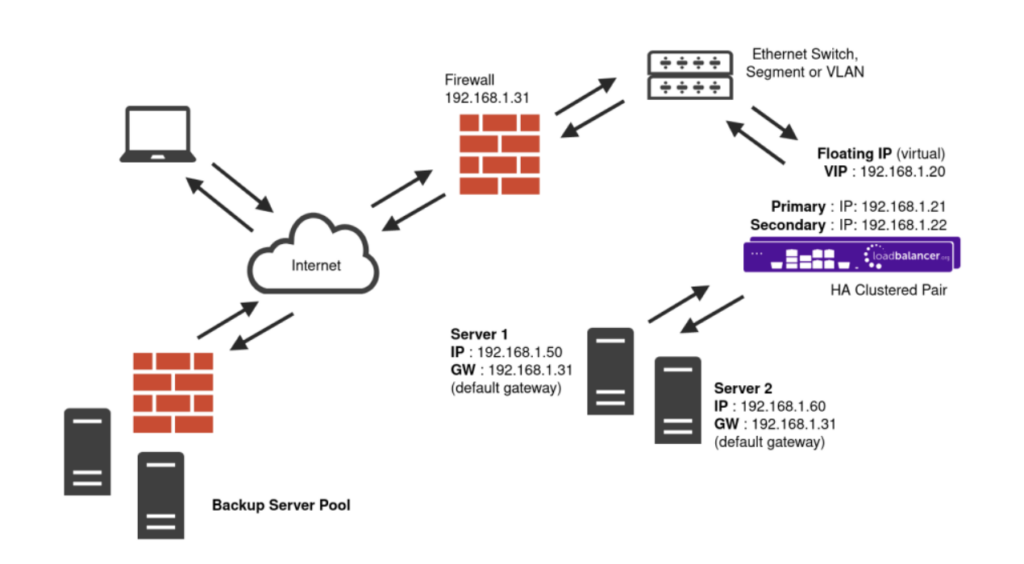
Because Layer 7 SNAT mode is a full proxy, any server in the cluster can be on any accessible subnet including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 7 SNAT mode is not transparent by default i.e. the Real Servers will not see the source IP address of the client, they will see the load balancer’s own IP address by default, or any other local appliance IP address if preferred (e.g. the VIP address). This can be configured per Layer 7 VIP. If required, the load balancer can be configured to provide the actual client IP address to the Real Servers in two ways:
- Either by inserting a header that contains the client’s source IP address, or
- By modifying the Source Address field of the IP packets and replacing the IP address of the load balancer with the IP address of the client.
Layer 7 SNAT mode can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth0 is normally used for the internal network and eth1 is used for the external network, although this is not mandatory. It does not require any mode-specific configuration changes to the load balanced Real Servers.
Port translation is possible with Layer 7 SNAT mode e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is supported. You should not use the same RIP:PORT combination for Layer 7 SNAT mode VIPs and Layer 4 SNAT mode VIPs because the required firewall rules conflict.
manual

Read Manual
Read manualblogs

Simplifying web application security with the Core Rule Set v3
Read blog
How to set up email notifications on your Loadbalancer.org appliance
Read blog
How to stop web form spam — use a simple honey pot trap in ModSecurity…
Read blogwhite paper

The OWASP Top 10 web application security threats
Read white paperother

Read deployment brief
Read other
Load balancing Microsoft Exchange
Read other
Load balancing Microsoft Always-On VPN
Read other

