Load balancing MinIO Server (Community Edition)
Benefits of load balancing MinIO Server
The three main benefits of load balancing a MinIO server cluster are:
- High Availability (HA): Load balancing significantly increases fault tolerance and guaranteed application uptime. If one MinIO server node fails, the load balancer automatically detects the issue using health checks and immediately redirects all client traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This prevents a single point of failure and ensures that the object storage service remains accessible and operational without interruption.
- Improved performance: By distributing incoming object storage requests (like PUT, GET, DELETE) across multiple MinIO nodes, a load balancer prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This leads to faster response times, reduced bottlenecks, and better resource utilization.
- Seamless scalability: Load balancing enables horizontal scaling by allowing you to add or remove MinIO server nodes dynamically without disrupting service. As your data and traffic demands grow, you can simply add new MinIO nodes to the cluster. The load balancer automatically starts distributing new requests to the added servers. Servers can be taken offline for maintenance, upgrades, or patching (rolling upgrades) by the load balancer, which temporarily directs traffic away from them.
About MinIO Server
MinIO Server is a high-performance open source S3 compatible object storage system designed for hyper-scale private data infrastructure.
MinIO can be installed on a wide range of industry standard hardware. It can run as a standalone server, but it’s full power is unleashed when deployed as a cluster with multiple nodes. From 4 to 32 nodes and beyond using MinIO federation.
Data is protected against hardware failure and data corruption using erasure code at the object level and bitrot protection. MinIO is highly available – a distributed cluster can loose up to half the disks on a single node and up to half the nodes and continue to serve objects.
The use of the Strict Consistency data model ensures that an exact copy of all data is available from all nodes. With Eventual Consistency, read operations could return old or stale data.
Why Loadbalancer.org for MinIO Server?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance MinIO Server
To create a MinIO cluster that can be load balanced, MinIO must be deployed in Distributed Erasure Code mode. This enables multiple disks across multiple nodes to be pooled into a single object storage server. Object data and parity is striped across all disks in all nodes. All objects can then be accessed from any node in the cluster.
Operating mode
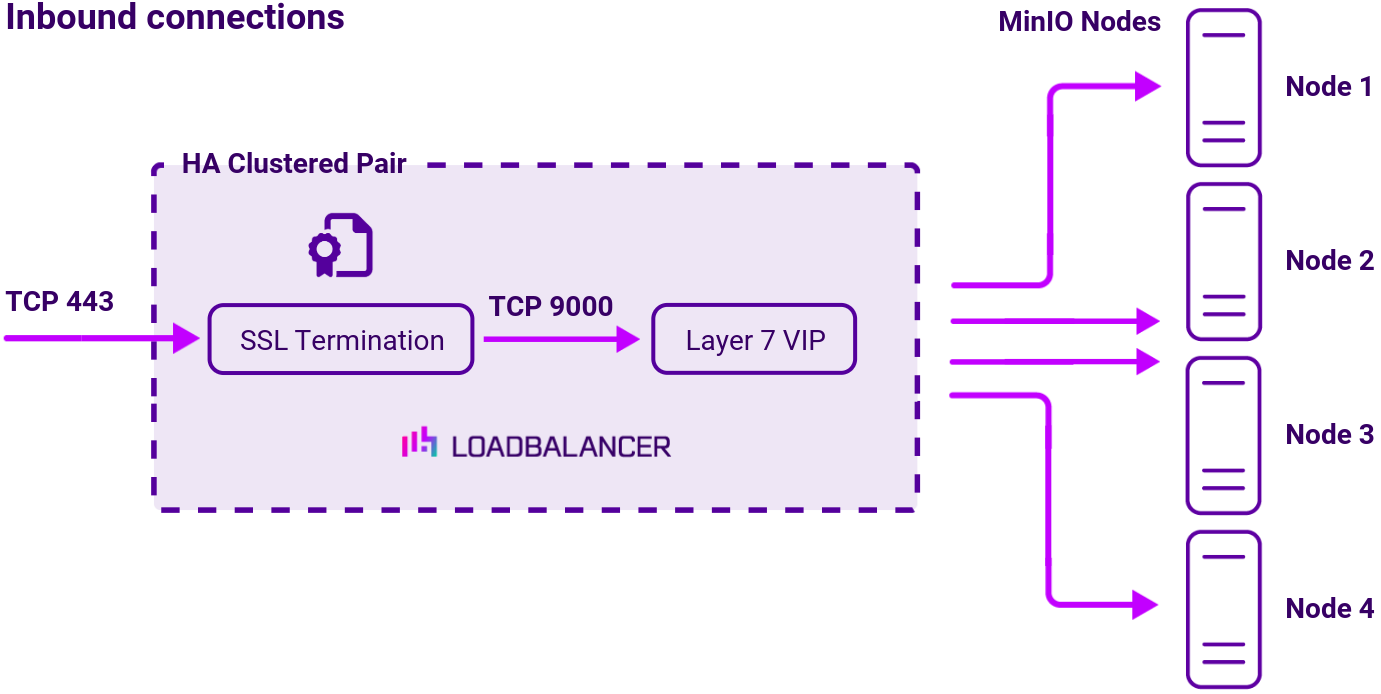
The load balancer is deployed at Layer 7. This mode offers high performance and requires no configuration changes to the load balanced MinIO Servers.
Timeouts
For MinIO Server, the load balancer’s client and server timeouts are set to 10 minutes.
Port requirements
The following table shows the port(s) that are load balanced:
| Port | Protocols | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 9000 | TCP | MinIO communications |
Note: Port 9000 is the default port for MinIO but this can be changed if required by modifying the node startup command – see the Deployment Guide more details.
SSL/TLS termination
To enable secure communication, SSL/TLS is terminated on the load balancer.
Health checks
As mentioned in the MinIO Monitoring Guide, MinIO includes 2 un-authenticated probe points that can be used to determine the state of each
MinIO node. In this guide, the heath checks are configured to read the readiness probe /minio/health/ready
Deployment concept
Note
The load balancer can be deployed as a single unit, although Loadbalancer.org recommends a clustered pair for resilience and high availability.