Load balancing Skype for Business

Useful resources
About Skype for Business
Skype for Business is a business class instant messaging, voice over IP (VoIP) and video collaboration tool by Microsoft. Since 2015, it has served as a replacement for Microsoft Lync (formerly Microsoft Office Communications Server).
Unlike the consumer version of Skype, the infrastructure for is hosted on Skype for Business Server. This is comprised a number of individual servers including, Frontend/Backend, Mediation, Director and Edge servers. Due to the number of servers and services provisioned, there is inherent complexity in the deployment. This requires a considered approach to high availability and distribution of user traffic.
Key benefits of load balancing
Here are a few key benefits:
- Ensures the application is always available
- Provides a stable, optimal performance
- Feature-rich highly resilient solution
- Scalability
Microsoft’s Enterprise solutions are at the heart of businesses everywhere. Loadbalancer.org is officially certified for all of Microsoft’s key applications which you can find here. More details on the Skype for Business components, how it works, and prerequisites for load balancing can be found in our deployment guide, available to view below.
Deploying Skype for Business with Loadbalancer.org appliances enables organizations to create a feature-rich highly resilient solution that ensures that wherever staff are located, and however they connect, they can depend on a platform that allows seamless communications wherever and whenever needed using the communications medium of their choice.
How to load balance Skype for Business
Loadbalancer.org appliances are configured to present a series of Virtual Servers (VIPs). These VIPs become the connection points for internal and external clients. The load balancer is then able to distribute requests to the Skype for Business servers that make up the various pools.
Here’s an example deployment architecture:
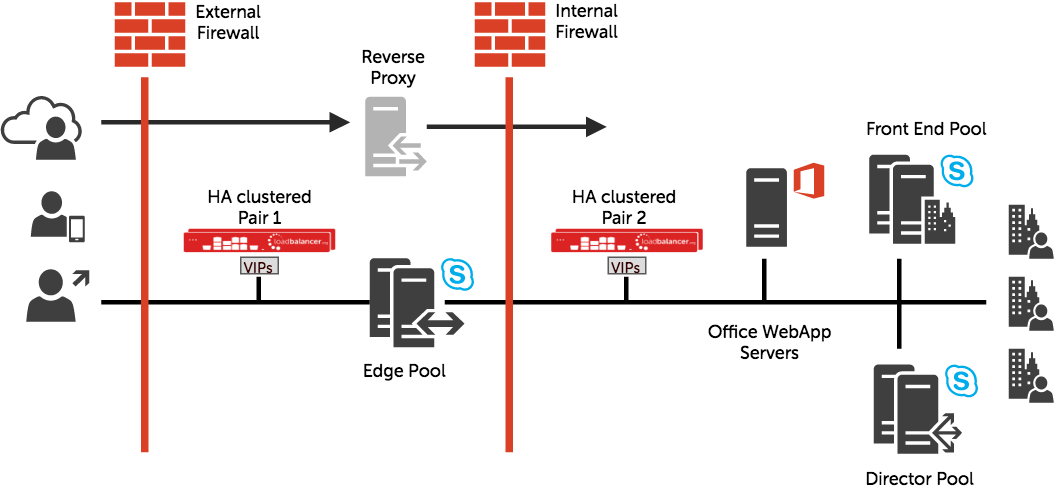
Example fully balanced deployment utilizing 2 HA pairs. HA pair 1 is used to load balance the external Edge, HA pair 2 is used to load balance the internal Edge and all other roles.
Direct Routing (DR) mode a.k.a. Direct Server Return (DSR) mode is not supported for Skype for Business.
UDP traffic must be configured with Layer 4 NAT mode.
TCP traffic can use either Layer 7 SNAT (Reverse Proxy) or layer 4 NAT.
Front End Servers Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/HTTP | Internal Web Services | Internal Web Services | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/DCOM/RPC | Various DCOM based operations | 135 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTPS | Internal Web ServicesUsed for HTTPS communication between the Focus (the Skype forBusiness Server component that manages conference state) and theindividual servers. | 443,444 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/TURN | Used for call admission control by the Skype for Business ServerBandwidth Policy Service | 448 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/TLS/MTLS/SIP | Various SIP based communication | 5061 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/SIP/TLS | Used by the Mediation Server for incoming requests from the Front EndServer to the Mediation Server | 5070 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/SIP/MTLS | Used for incoming SIP requests for the Response Group application, Attendant (dial in conferencing), the Skype for Business Server Conferencing Announcement service (that is, for dial-in conferencing), the Call Park application | 5071, 5072, 5073, 5075 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/SIP | Used for incoming SIP requests for the Audio Test service | 5076 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP | Used for call admission control by the Bandwidth Policy service for A/VEdge TURN traffic | 5080 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTPS | External Web Services – from Reverse Proxy | 4443 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTPS | External Web Services – from Reverse Proxy | 8080 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
Director Servers Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/HTTPS | Internal Web Services | 443 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTPS | Inter-server communication between Front End and Director | 444 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/TLS/MTLS/SIP | Internal SIP communications between servers and for client connections | 5061 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTP | External Web Services – from Reverse Proxy | 4443 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
| TCP/HTTP | External Web Services – from Reverse Proxy | 8080 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP and cookie insertion capabilities) |
Edge Servers (External Interface) – Access (SIP) Service Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/STUN | Audio/Visual service | 443 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| UDP/STUN | Audio/Visual service | 3478 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| TCP/MTLS/SIP | Access (SIP proxy) service | 5061 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| TCP/MTLS/SIP | Audio/Visual authentication service | 5062 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
Edge Servers (External Interface) – Access (SIP) Service Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/TLS/STUN/SIP | Access (SIP proxy) service | 443 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| TCP/MTLS/SIP | Access (SIP proxy) service | 5061 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| TCP/XMPP | Access (XMPP Proxy) service | 5269 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
Web conference service Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/TLS/STUN/SIP | Web conferencing | 443 | Layer 7 SNAT – (Source IP persistence) |
Audio/Visual Service Protocols Table
| Protocol | Role | Ports | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/TLS/STUN/SIP | Access (SIP proxy), Web Conferencing, Audio/Visual services | 443 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
| UDP/STUN | Audio/Visual service | 3478 | Layer 4 NAT – (Fast Load balancing throughput Source IP persistence)Layer 7 SNAT – (Flexible, Source IP persistence) |
deployment guide

Microsoft Skype for Business Deployment Guide
Read deployment guidemanual

Administration manual v8
Read manualcase study

Microsoft Exchange - Sunfield Children’s Home
Read case studyblogs

How Scomis improves the scalability and performance of its Hosted Application Service
Read blog
Load Balancing Exchange 2013
Read blogother

Load balancing requirements for Skype for Business
Read other
How to load balance Microsoft applications
Read other
https://devcentral.f5.com/s/articles/the-hopefully-definitive-guide-to-load-balancing-lync-edge-servers-with-a-hardware-load-balancer
Read other

