Load balancing medical imaging systems: PACS, VNA, DICOM, XDS & HL7

Useful resources
About Load balancing medical imaging systems
Medical imaging provides a non-invasive procedure of taking images with a clinical application, using a variety of imaging modalities to provide a specified diagnostic picture of the body. Various modalities are used, such as CT, MRI, PET, Ultrasound & X-Ray.
A critical element in patient care, access to diagnostic images is crucial at all times, especially when demand is unpredictable. Load balancing provides a fast, redundant and scalable architecture for the transfer, storage and retrieval of images.
Key benefits of load balancing
In an industry where uptime saves lives, our extensive experience means we can design unbreakable solutions to enterprise imaging’s unique challenges. Loadbalancer.org are specialists in delivering ultra-reliable, scalable medical imaging applications. Load balancing provides organizations with a solution that is:
- high-performing
- ultra-reliable
- highly available
- scalable
How to load balance medical imaging systems
Failures can be costly to the healthcare system and to patients, so achieving zero downtime is a key consideration. Loadbalancer.org appliances monitor the status of medical imaging storage and applications servers (health checks) and seamlessly directs traffic to the healthy, online or least loaded servers.
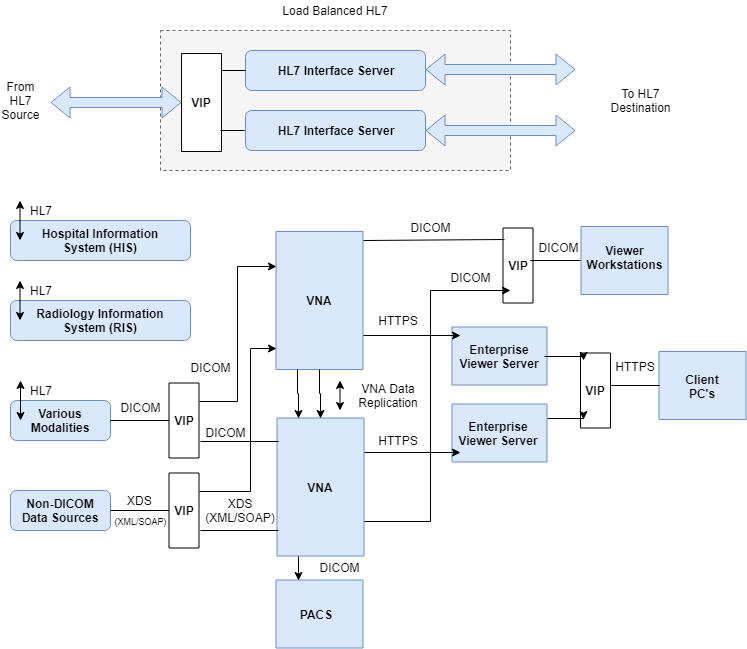
Example of a highly available system that utilizes system component and load balancing
Typical Implementation
A standard imaging deployment combines fast, highly available storage with unrestricted retrieval of images using our ultra-fast Layer 4 Direct Routing (DR) mode of operation. In a large hospital environment, peak image retrieval traffic volumes can be more than 5x the volume of storage traffic. The example outlined here demonstrates the benefits of DR and why our products are so well suited to medical imaging requirements.
| Imaging | Total Images | MB/image | MB/study (RAW) | Number of studies/year | Storage per study type (MB) |
| Cardiology imaging device | 22 | 22.11 | 486.42 | 10,000 | 4,864,200 |
| CT – Multi-slice imaging device | 400 | 0.52 | 208.00 | 20,000 | 4,160,000 |
| CT – 64-slice imaging device | 2000 | 0.51 | 1020.00 | 100,000 | 100,000,000 |
| CT – 128-slice imaging device | 4000 | 0.51 | 2040.00 | 200,000 | 200,000,000 |
| Fluoroscopy imaging device | 24 | 1.96 | 47.04 | 50,000 | 2,352,000 |
| Mammography imaging device | 4 | 26.00 | 104.00 | 20,000 | 2,080,000 |
| MRI – Magnetic resonance imaging device | 400 | 0.18 | 72.00 | 10,000 | 720,000 |
| Ultrasound imaging device | 40 | 0.75 | 30.00 | 30,000 | 900,000 |
| Total | 440,000 | 315,076,200 |
In this example of 440k studies/year we have a yearly storage requirement of 315TB, which equates to 863GB per day, or a data rate of 1.9GB/s. The below table demonstrates how the retrieval traffic exceeds 11GB/s but, by utilizing DR mode, traffic on the return path bypasses the load balancer directly to the client, meaning there is no packet flow limitation. In practice, this means our entry-level hardware provides reliable image retrieval on a deployment of this size.
| Number of stations | Studies/hour | Study size MB (avg) | Data rate Mbit/s | |
| Reporting stations traffic | 45 | 100 | 1020 | 10,200 |
| Concurrent users traffic | 1000 | 10 | 30 | 667 |
| CDR PACS users | 600 | 40 | 60 | 533 |
| Total traffic | 11,400 |
Below are examples of the systems, standards and protocols that support load balancing:
| Protocol | Description |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) provides storage and access to diagnostic images from multiple modalities. |
| VNA | Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA) is an archival system, capable of storing images in a standard format. |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a standard for storing and transmitting medical images. |
| HL7 | Health Level-7 (HL7) is a set of standards for transfer of data between software applications used in healthcare. |
| XDS | Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) is a standard for sharing of patient Electronic Healthcare Records. |
Load balanced ports and services
The following tables shows the typical ports/services that are load balanced:
| Port | Protocols | Use |
| 104 | TCP/DICOM | Exchange of images and related information |
| 11112 | TCP/DICOM | Exchange of images and related information |
| 2575 | TCP/HL7/MLLP | Communication between healthcare IT systems |
| 443 | TCP/HTTPS | Client viewer connectivity |
| 17035 | TCP/XDS/SOAP/XML | XDS repository/registry |
Loadbalancer.org specializes in load balancing healthcare applications and is the only vendor with native support. In order to support such an array of different applications, we use a variety of load balancing methods including Layer 4 DR, Layer 4 NAT and Layer 7 SNAT modes.
Experts in load balancing medical imaging applications
You need a vendor who’s experienced in supporting the healthcare industry to the highest standards and who has worked with some of the world’s leading medical imaging vendors. Loadbalancer.org is committed to understanding your business, and partnering with you to meet your goals. Our team of application delivery specialists will help design and simplify your architecture, as well as providing round-the-clock support.
Vendors we’ve worked closely with





deployment guide

Medical Imaging & Information System Protocols Deployment Guide
Read deployment guidemanual

Administration manual v8
Read manualcase studies

NHS Trust, North Lincs and Goole - Improving the resilience and availability of medical imaging systems
Read case study
Fujifilm - Partnership ensures highly available and reliable medical imaging systems
Read case studyblogs

How to configure a DICOM ECHO health check for medical imaging systems
Read blog
I didn't realise NTP was so important for Medical Imaging Systems like PACS and VNA
Read blog
Strengthening the radiology workflow
Read blogwhite paper

The pivotal role of the load balancer in PACS migrations
Read white paper

